Causes, symptoms and treatment techniques of glaucoma
Glaucoma is a chronic eye disease known as the "vision thief". Without any aura, early glaucoma has no significant pain or symptoms, so it is difficult to detect and is only noticed when the patient's vision is narrowed. However, when the patient notices a narrowed visual field, his or her eye has suffered irreversible damage. According to the Hong Kong Society of Ophthalmology, 23% of patients who lose their vision are blinded by blindness; People with farsightedness and older than 40 years are at high risk for acute glaucoma.
Glaucoma is caused by excessive pressure in the eyeball, resulting in progressive damage to the anterior chamber, retina, and optic nerve fibers. However, there are patients with intraocular pressure in the normal range (10-21mmHg), but the optic nerve is still unable to withstand the pressure and is damaged, resulting in narrowed vision. Early vision loss usually begins in the peripheral field of view and ends up with only the central part. Without proper treatment, vision can gradually decline or even be completely lost.
Learn more about the causes behind glaucoma
Under healthy conditions, our eyes continuously produce a fluid called "aqueous humor", and to maintain healthy intraocular pressure, the anterior aqueous fluid must be drained from the eye. Eye obsession is caused by high intraocular pressure, which leads to gradual damage to the optic nerve. However, there are patients with intraocular pressure in the normal range (10-21mmHg), but the optic nerve is still unable to withstand the pressure and is damaged, resulting in narrowed vision. Early vision loss usually begins in the peripheral field of view and ends up with only the central part. Without proper treatment, vision can gradually decline or even be completely lost.
Ophthalmologist Tang Wenjie explains the symptoms of glaucoma
Illustrated glaucoma symptoms

Types of glaucoma
Glaucoma can be divided into different types according to its characteristics and etiology. These include chronic glaucoma and acute glaucoma.
- Chronic glaucoma
- In the early stages, there are no obvious symptoms, and the patient may not notice any signs. As the disease progresses, the patient's visual field will gradually shrink, and eventually only the central vision will remain, and the peripheral vision will be lost, forming the so-called "tunnel vision". If the condition continues to deteriorate, it may lead to complete blindness.
- Acute glaucoma
- Intraocular pressure suddenly rises and obvious symptoms such as blurred vision, rainbow circles when looking at light, red eyes, corneal opacity, severe eye pain, headache, nausea and vomiting. Acute glaucoma, if left untreated, can even lead to permanent vision loss within a day.
Depending on the etiology, glaucoma can also be divided into two categories: primary and secondary.
- Primary glaucoma
- There are no obvious causes, including open-angle glaucoma and angle-closure glaucoma
- Open-angle glaucoma is when the anterior chamber angle is open, but the optic nerve is gradually damaged due to increased intraocular pressure. In the early stages, most patients fail to detect any symptoms and aura.
- Angle-closure glaucoma is characterized by abnormal closure of the anterior chamber angle, resulting in obstructed outflow of aqueous humor and increased intraocular pressure. If the anterior chamber angle closes more slowly and intraocular pressure rises more slowly, the patient may not experience any symptoms.
- There are no obvious causes, including open-angle glaucoma and angle-closure glaucoma
- Secondary glaucoma
- Increased intraocular pressure caused by other conditions such as mature cataracts, iritis, bleeding inside the eyeball, tumors, trauma, postoperative complications, and inappropriate use of steroid medications. There are many types of glaucoma, but early detection and prompt treatment are key to reducing the risk of visual impairment.
Different kinds of glaucoma symptoms
Wondering if you have glaucoma? In addition to comparing the symptoms of different types of eye diseases, we can also gain insight into different types of glaucoma symptoms.
Early chronic open-angle glaucoma often has no obvious symptoms, but as the disease progresses, patients may gradually develop loss of peripheral vision.
Early symptoms of angle-closure acute glaucoma may include eye pain, redness, blurred vision, eye swelling, and nausea and vomiting. An attack of acute angle-closure glaucoma may cause symptoms such as acute, severe eye pain, headache, nausea and vomiting, blurred vision, and seeing halos.
Causes and risk factors of glaucoma
Be 40 years of age or older
Advanced age is an important risk factor for glaucoma. The prevalence of glaucoma increases exponentially with age. People over the age of 60 have a 6-fold increased chance of developing glaucoma.
Hypertension.
People with high blood pressure are twice as likely to develop "normal intraocular pressure glaucoma" than others. High blood pressure can impair the regulatory system of blood circulation in the eyeball, causing the blood in the eye to function improperly. Therefore, even if the intraocular pressure is within the normal range, high blood pressure can accelerate the rate of optic nerve degeneration.
Diabetes.
The results showed that people with diabetes were twice as likely to develop glaucoma, mainly open-angle glaucoma, compared to non-diabetics.
Suffering from cardiovascular disease
People with cardiovascular disease are more likely to develop glaucoma. Although hyperlipidemia does not directly cause eye lesions, studies have shown that hyperlipidemia is directly proportional to the increase in intraocular pressure, thereby increasing the risk of glaucoma.
Have been prescribed for taking or applying steroids
Long-term steroid use can lead to an increase in intraocular pressure, which in turn can lead to steroid-induced glaucoma. Long-term use of steroids can block the aqueous humor drainage hole of the eyeball, reducing the rate of aqueous humor drainage, which in turn leads to increased intraocular pressure. However, once steroid use is stopped, IOP can drop to the normal range in most patients.
Family genetic history of glaucoma
Having a family case of glaucoma carries a higher risk. Open-angle glaucoma is the most common hereditary form of glaucoma. If an immediate family member has glaucoma, your risk of developing the disease increases by 4 to 9 times.
Eye injury.
When the eye is hit by a hard object, especially a blunt trauma, it may cause bleeding from the eyeball structures such as the iris, blocking the flow of aqueous humor, which in turn leads to increased intraocular pressure, which in turn leads to glaucoma.
Long-term migraine
Long-term migraines are closely associated with glaucoma. Glaucoma can generally be divided into acute and chronic forms, and most cases that cause migraines are chronic glaucoma. On the other hand, migraine is sometimes mistreated along with acute angle-closure glaucoma because the exit aperture of the anterior chamber of the eye is blocked for a short period of time, resulting in a rapid rise in intraocular pressure, which may be accompanied by corneal edema, which can trigger severe headache symptoms. This condition is often mistaken for migraine, which delays the timely treatment of glaucoma.
Deep distance/nearsightedness
Deep myopia and farsightedness are also one of the causes of glaucoma. Farsighted patients are prone to extra-corner atresia glaucoma, and high myopia is also one of the causes of chronic open-angle glaucoma. Studies have also pointed out that myopic eyes are more susceptible to increased intraocular pressure. In particular, people with more than 500 degrees of myopia and increased intraocular pressure are more likely to have narrowed visual fields.
Sleep apnea
Recent literature studies have pointed out that there is a relationship between sleep apnea and glaucoma. It is possible that the patient has a lack of oxygen during sleep, which in turn affects the blood circulation around the eyeball, resulting in hypoxia of the optic nerve, which in turn leads to the gradual deterioration of vision.
Glaucoma examination.
Why should I get regular glaucoma tests?
Glaucoma is a common eye condition that gradually damages the optic nerve, which can eventually lead to vision loss. However, early chronic glaucoma often has no obvious symptoms, and many patients do not realize they are affected until the disease progresses to a later stage, and once the optic nerve is damaged, it cannot be reversed. Therefore, regular glaucoma check-ups are essential for early detection and control of glaucoma. It can help with early diagnosis and treatment to prevent vision loss.
Suitable objects
- 18 years old or above (especially 40 years old or above)
- People with deep myopia (600 degrees or above)
- diabetic
- There is glaucoma in the family
- Trauma to the eye
- Glaucoma is suspected
Glaucoma comprehensive examination range
1. Inquire about medical records and medical records
Understand the symptoms of vision problems and eye diseases
2. Visual acuity and refractive power examination
Through different procedures and instruments, the patient's visual condition can be accurately determined, including myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism and presbyopia.
3. Intraocular pressure measurement
Intraocular pressure is one of the main indicators of glaucoma. Doctors usually use a non-contact manometer or an instrument that applies light pressure to measure intraocular pressure. This procedure is usually painless and can be done in an eye clinic.
4. Optic nerve examination
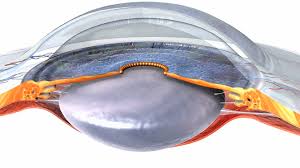
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY (OCT) PLAYS AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF GLAUCOMA. IT IS A NON-INVASIVE OPTICAL DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUE IN WHICH DOCTORS USE THIS HIGH-RESOLUTION OPTICAL ANALYSIS METHOD TO EXAMINE THE EYE TO DETERMINE IF THERE ARE SIGNS OF OPTIC NERVE DAMAGE. THROUGH ADVANCED EQUIPMENT, THE HEALTH STATUS OF THE OPTIC NERVE CAN BE ASSESSED IN MORE DETAIL AND A MORE COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT CAN BE PROVIDED FOR EARLY DETECTION OF GLAUCOMA. DAMAGE TO THE OPTIC NERVE CAN BE DETECTED AT AN EARLY STAGE AND APPROPRIATE TREATMENT CAN BE FORMULATED.
5. Visual field test
A visual field test can help your doctor assess the integrity of your visual field and any potential visual field defects. This test is usually performed using an automated perimetry instrument, where the patient looks at a specific spot and detects changes in the brightness of the spot in all directions. This can help doctors know if their field of vision is impaired.
6. Microscopic examination
Endoscopy involves the use of lenses to assess the anterior and posterior structures of the eye. Doctors can check the health of areas such as the iris, lens, and retina through microscopy. This test can provide important information about the internal structure of the eye.
7. Analysis and construction
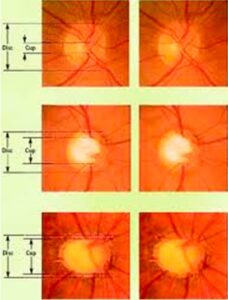
Glaucoma treatment techniques
Prescription eye drops are one of the common treatments for glaucoma. Eye drops can be used to control intraocular pressure levels to the appropriate target range, protect optic nerve tissue and reduce further visual impairment. As a non-invasive treatment, eye medication has fewer side effects and is safer than laser and surgical treatments. Many glaucoma eye drops are now available in a combined formula, allowing patients to take only one drop a day.
If glaucoma cannot be controlled with medical treatment, patients may consider laser and surgical treatment, such as trabeculectomy, drainage surgery, catheter implantation, ciliary photocoagulation or cryoplasty, argon laser periiroplasty and minimally invasive glaucoma surgery.
- Trabeculectomy is a surgical procedure that reduces intraocular pressure by removing part of the trabecular tissue to increase the drainage of the aqueous humor.
- Drainage surgery creates a new drainage channel in the eye to facilitate the drainage of aqueous humor.
- Catheter implantation involves placing a drainage catheter in the eye to direct the flow of aqueous humor.
- Cyclophotocoagulation or cryosurgery is the destruction of ciliary body tissue by laser or cryotechnology, reducing the production of aqueous humor and thereby reducing intraocular pressure.
- Argon laser iris periplasty uses argon laser to expand the outflow channel of aqueous humor and increase the outflow of aqueous fluid.
A new option for patients with mild to moderate glaucoma: the latest glaucoma treatments
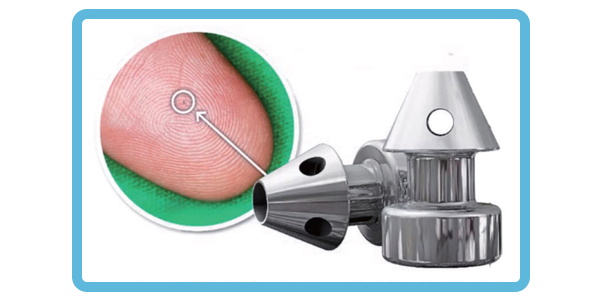
IN RECENT YEARS, MINIMALLY INVASIVE GLAUCOMA SURGERY (MIGS) HAS BEEN USED, MAKING IT LESS INVASIVE THAN TRADITIONAL GLAUCOMA SURGERY, THUS REDUCING THE RISK OF COMPLICATIONS AND PROVIDING NEW OPTIONS FOR PATIENTS WITH MILD TO MODERATE GLAUCOMA. MINIMALLY INVASIVE GLAUCOMA SURGERY PROVIDES GREATER SAFETY AND FASTER RECOVERY TIMES, WHILE REDUCING THE BURDEN ON PATIENTS WITH GLAUCOMA DRUGS.
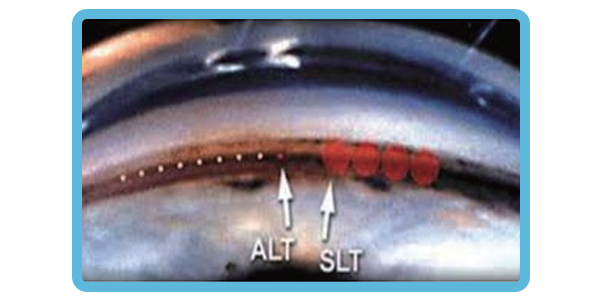
SELECTIVE LASER TRABECULOPLASTY (SLT) IS A CLINIC PROCEDURE THAT REDUCES INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE IN GLAUCOMA PATIENTS. THE LASER SHINES THROUGH A SPECIAL MIRROR INTO THE DRAINAGE SYSTEM OF THE EYE, WHERE BIOCHEMICAL CHANGES ARE STIMULATED, THEREBY IMPROVING THE OUTFLOW OF AQUEOUS HUMOR FROM THE EYE. BECAUSE SLT HAS EXCELLENT "BENEFITING FROM RISK" PROPERTIES, SLT IS OFFERED AS AN OPTION EARLY IN THE TREATMENT STRATEGY FOR GLAUCOMA, INCLUDING AS THE PRIMARY TREATMENT.
STUDIES COMPARING SLT AND EYE DROPS AS PRIMARY THERAPY FOUND SIMILAR TREATMENT EFFECTS BETWEEN THE TWO GROUPS. ALTHOUGH SOME PATIENTS STILL NEED EYE DROPS AFTER SLT, THEY NEED FEWER EYE DROPS TO CONTROL THEIR GLAUCOMA.
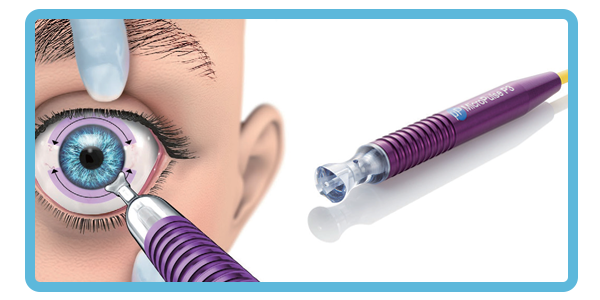
The MicroPulse P3 Glaucoma Device (MP3), provided by the CYCLO G6 Glaucoma Laser System, utilizes non-pulsed, repeatable and predictable MicroPulse®technology to provide innovative annular condensation that destroys ciliary body tissue and reduces the production of aqueous humor to reduce intraocular pressure.
Glaucoma FAQs
What can I eat to prevent glaucoma?
It is recommended to increase your intake of vegetables and fruits containing vitamins, minerals and antioxidant nutrients, such as kale, carrots and peaches. In addition, eating nitrogen-rich foods, such as dark green vegetables, can also help reduce the risk of glaucoma.
How Long After Diagnosis of Glaucoma Can I Go Blind?
Glaucoma does not necessarily cause blindness, and can be effectively controlled if the patient receives stable treatment. The chance of blindness caused by glaucoma is about 10% to 25%, and in the case of acute glaucoma, if left untreated, patients with acute glaucoma may be at risk of blindness within a few days.
Chronic glaucoma usually has no obvious symptoms in the early stages. When problems such as blurred vision, inability to see objects clearly at an angle, and stepping on stairs usually indicate that glaucoma has entered an advanced stage, and patients may face a crisis of blindness within 3 to 5 years.
Can glaucoma be cured?
There is currently no complete treatment for glaucoma, but as long as the correct diagnosis and treatment can be carried out at an early stage and in close cooperation with an ophthalmologist, the good condition of the eye can be maintained to the greatest extent.
How is glaucoma detected early?
Early glaucoma lacks obvious symptoms, and once the patient notices that his field of vision is narrowed, the eye has suffered irreversible damage. Therefore, it is recommended that adults should have a comprehensive eye examination every one to two years to check intraocular pressure, cornea, and other eye health conditions so as not to miss the opportunity to control the disease.



How to improve the degree of presbyopia?
Presbyopia is a natural age-related phenomenon of aging, and it is due to the eyeballs
Consultation registration
